What is spirulina?
Spirulina is currently one of the most popular nutritional foods in the world; it is known as a high-quality source of plant protein for vegetarians and a source of Vitamins.
As early as the 1970s, food shortages and famines became an international crisis. Protein is the main nutrient that people are most concerned about. Many countries in Africa face problems such as malnutrition and severe protein inadequacy. So much work has been done on protein deficiency. Soybean was the first crop to be included in the solution of protein deficiency, but as land pollution increased and people’s awareness of environmental protection and sustainable development increased, algae-derived proteins began to enter the eyes of scientists, and they soon discovered spirulina.
Algae has been farmed and consumed by consumers around the world for many years. It is dry food, rich in nutrients, and has been used as food and even livestock feed. In 1974, the World Health Organization declared it the “best food of the future” to fight malnutrition, especially among children.
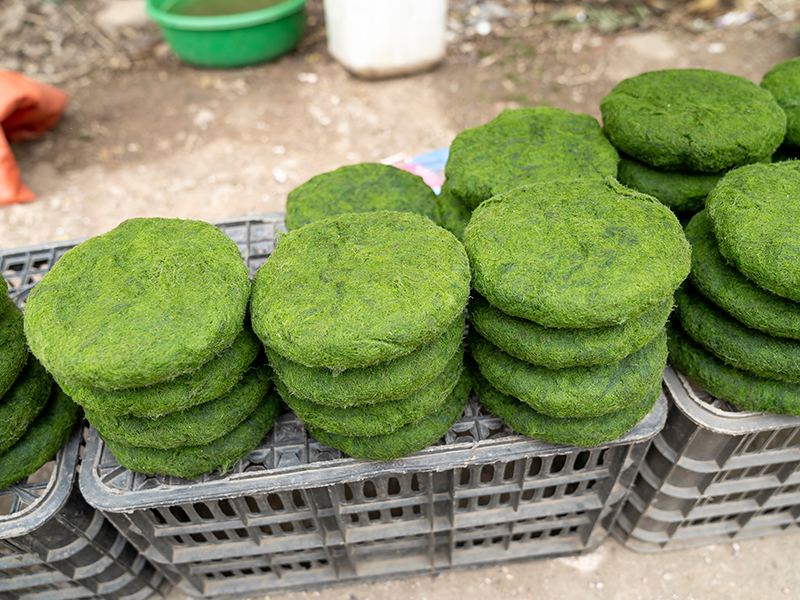

African minorities make spirulina juice into a cake
Currently, researchers worldwide are studying the health benefits of spirulina. In many clinical trials, spirulina has been shown to fight certain types of cancer cells, reduce cholesterol levels, and stimulate weight loss, and this is just the tip of the iceberg.
12 health benefits of spirulina
1.High nutrition
Spirulina usually comes in powder or tablet form. 1 teaspoon of the powder is about 2 grams.
1 teaspoon (2 grams) of spirulina powder has:
1.2-1.5 g protein, 4-8 mcg vitamin E, 0.4-0.5 g carbohydrate, 0.12-0.16 g fat, 0.1-0.16 g dietary fiber, 18-30 mg potassium, 16-20 mg phosphorus, 6-8 mg chromium, 2-4 mg of carotene, 0.1-0.16 mg of vitamin C, 0.6-1 mg of vitamin B1, 16-40 mg of chlorophyll, 6-8 mg of carotenoids, etc.
“Spirulina is rich in multivitamins but does not contain vitamin B12. Spirulina is always advertised online as being rich in vitamin B12 and can be a good dietary supplement for vegetarians. However, the study found that spirulina contains a compound with a structure close to that of vitamin B12. These substances will be mistaken for vitamin B12 by the instrument for immunological analysis, but in fact, these substances do not play a nutritional role in B12. According to the most accurate method, spirulina is vitamin B12-free.”
2.Enhance immunity
The immune system is a complex network involving several cell types, tissues, and organ systems. Spirulina is rich in phytonutrients and unique polysaccharides and has been shown to stimulate immune function.
Spirulina positively affects the immune-related activities of the bone marrow, thymus, and spleen. Phycocyanin and its polysaccharides in spirulina also increase the production of white blood cells (immune system cells). Specifically, spirulina can increase the number and activity of macrophages, white blood cells that devour pathogens, and early cancer cells such as Pacman.
Spirulina also can destroy the activity of cancer cells, so it can kill some viruses and tumors. Spirulina can protect individual cells of the immune system from damage and toxins so that they can perform their disease resistance.
3.Spirulina balances blood lipids
Spirulina and phycocyanin can help the body lower blood pressure, prevent LDL cholesterol oxidation, and reduce inflammation. Spirulina has been found in several human trials to balance cholesterol and blood lipids.
4.Protect the brain and neurons
Spirulina has been shown to protect brain cells and the vascular network that surrounds them from damage. Neurocognitive disorders, also known as dementia, are caused in part by years of oxidative damage. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of spirulina may help prevent dementia like other phytonutrients and plant foods rich in antioxidants.
Spirulina can also help protect microglia by reducing inflammation. Spirulina can also help maintain brain function and flexibility by supporting pathways involving BDNF and CREB, both of which support healthy brain function.
5.Reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease
The cell membrane consists of a fatty structure called a phospholipid, which is susceptible to oxidative damage. This is called lipid peroxidation and is a driver of many chronic diseases. One of the most common examples is the oxidation of “bad” LDL cholesterol, a key first step in an inflammatory disease called atherosclerosis. Reducing LDL damage is an important strategy to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Interestingly, the antioxidants in spirulina are effective in reducing lipid peroxidation in humans and animals.
In a small study of 37 patients with type 2 diabetes, 8 grams (just over 1 tablespoon) of spirulina a day significantly reduced markers of oxidative damage. It also increases the level of antioxidant enzymes in the blood.
6.Maintain healthy blood pressure
High blood pressure is a recognized risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as stroke and renal failure. Spirulina daily intake of 4.5 grams (2.5 teaspoons) has been shown to reduce blood pressure in normal blood pressure people, which may be produced by increasing the production of nitric oxide, a gas produced by blood vessels that can Relaxation and swelling.
Other clinical studies have shown that spirulina has a blood pressure-lowering effect. Diastolic blood pressure in particular; when the heart is at rest between beats, the lower of these two numbers can measure pressure in the blood vessels. Diastolic blood pressure readings are considered a more important item when assessing vascular health in situations of hypertension. Diastolic blood pressure was significantly reduced in people taking spirulina supplements.
7.Anti-cancer properties
Studies show that in a human trial of 87 tobacco-chewing agents, taking 1 year (1 teaspoon (1/2 teaspoon) of spirulina effectively helped to solve 45% of patients with oral leukoplakia. This implies that it may be reducing Oral cancer plays a role because oral leukoplakia (also known as oral submucosal fibrosis or OSMF) is a condition in which smokers and chewers form white plaques on their endometrium. This tobacco-related patch is associated with oral and throat cancers and is associated with an increased risk.
In another study of 40 individuals with OSMF / oral leukoplakia, 1 g (1/2 teaspoon) of spirulina per day caused greater improvement in OSMF symptoms than the drug Pentoxifylline.

8.Support liver health
Like many phytonutrients found in many plant foods, phytonutrients of spirulina support good liver health by reducing inflammation. In a human study, 4.5 grams (2 teaspoons) of spirulina per person helped to improve the symptoms of fatty liver disease.
9.Helps reduce the symptoms of allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal cavity) is the most common allergic reaction to environmental allergens such as pollen, animal hair, or dust. This is also a major part of asthma. In a clinical study of 127 people, 2 g (1 teaspoon) of spirulina a day reduced all symptoms of allergic rhinitis compared to placebo.
10. Spirulina helps prevent anemia
There are many different forms of anemia, including malignant anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency. The most common feature is a decrease in hemoglobin or red blood cells in the blood.
A study of 40 elderly people with a history of anemia found that spirulina supplements increased the hemoglobin content of red blood cells and improved immune function. Although spirulina is not a separate treatment, it may be an adjunct strategy.
11.Improve endurance and strength
Exercise-induced oxidative damage is a major cause of muscle fatigue. Some plant-based foods contain phytonutrients that can help minimize the harm to athletes and athletes. Spirulina can improve muscle strength and endurance. It has been proven to improve exercise energy output and prevent fatigue. It is impressive that in a small study of 18 adult men, both short-term and long-term supplementation with spirulina improved exercise and delayed fatigue.
12.Balance blood sugar
Spirulina has some interesting research on diabetes management. A meta-analysis of 12 clinical trials found that spirulina can effectively reduce fasting blood glucose, and other studies have shown that spirulina can improve insulin sensitivity.
In some cases, it performs better than popular diabetes drugs, including metformin. In a two-month study of 25 patients with type 2 diabetes, 2 grams of spirulina daily reduced blood glucose levels significantly. HbA1c is a marker of long-term blood glucose levels, from 9% to 8%, which is very important and is considered to have clinical significance.
Spirulina has shown many health benefits, including lowering blood pressure, improving blood sugar and insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of certain cancers, improving blood lipid ratios, supporting brain health, and more.
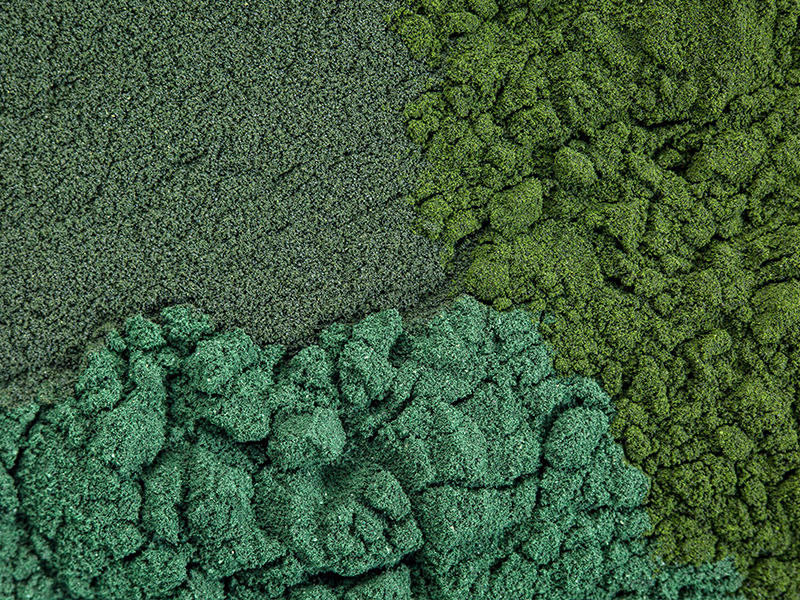

Spirulina vs. Chlorella
Chlorella is another vegetative algae. Indeed, spirulina and chlorella are often confused. Chlorella is also an alga, but it can only grow in freshwater, not in saltwater like many blue-green algae.
Chlorella is also a good source of protein, fiber, chlorophyll, vitamins, and minerals.
Spirulina is a much larger plant with the iconic blue-green color, while chlorella is a nearly dark green solid. Spirulina and chlorella also have different nutritional components. Spirulina provides more amino acids, iron, protein, and vitamins than green algae.
Application of spirulina
Spirulina can be used as a food additive to supplement amino acids and vitamins and improve the utilization of protein. Spirulina foods that have been developed so far include powders, tablets, capsules, instant granules, beverages, oral liquids, beer, nutritional pasta, ice cream, candy, chocolate, and biscuits.
Spirulina is rich in active substances and has special medical and protective effects on a variety of diseases. Spirulina can be used to prevent cancer, anti-aging, and enhance the body’s multiple functions.
Spirulina is also an excellent feed material, with high protein content, rich nutrition, high digestive absorption, and other significant features. Spirulina as feed can promote the growth of animals, improve production performance, reduce feed consumption; increase the breeding rate of breeding poultry and breeding animals; increase the survival rate of aquatic animals in Haizhen, raise the cost of the nursery, and increase the immunity and vitality of larvae, It can also make ornamental fishes brighter in color.